What is Manufacturing Equipment? Types, Uses, and Benefits Explained
Manufacturing equipment plays a pivotal role in modern industrial processes, serving as the backbone of production lines across various sectors. As industry expert Dr. Emily Carter, a leading authority in manufacturing technologies, aptly states, “The efficiency and precision of manufacturing equipment can significantly determine a company’s competitiveness in the market.” This assertion underscores the necessity for businesses to invest in state-of-the-art machinery that not only enhances productivity but also ensures quality and safety in manufacturing operations.
The landscape of manufacturing equipment is vast and varied, encompassing tools ranging from simple hand tools to complex robotics and automation systems. Each type serves specialized functions, contributing to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of manufacturing processes. Understanding the different types and their applications can give businesses a competitive edge and optimize their workflow.
As we delve deeper into the various types, uses, and benefits of manufacturing equipment, it becomes evident that the right investment in equipment is crucial. By equipping themselves with the latest technologies, manufacturers can improve output, reduce waste, and adapt swiftly to changing market demands, ensuring sustainability and growth in an ever-evolving industry.

What is Manufacturing Equipment? An Overview of Key Definitions
Manufacturing equipment refers to a variety of tools and machines used in the production process to convert raw materials into finished products. These tools can range from simple hand-operated devices to complex automated machinery. At its core, manufacturing equipment is essential for efficiency, precision, and scale in production. It plays a critical role in various industries, including automotive, electronics, and textiles. Understanding the various types of manufacturing equipment and their specific applications can help businesses optimize their operations and enhance productivity.
The main categories of manufacturing equipment include cutting machines, assembly machines, packaging machines, and quality control devices. Cutting machines, for instance, are crucial for shaping materials, while assembly machines help streamline the process of putting together parts. Packaging machines play an important role in preparing products for shipment, ensuring that they are secure and ready for sale. Additionally, quality control equipment is vital for maintaining standards and ensuring that products meet safety and regulatory requirements.
By leveraging the right manufacturing equipment, businesses can achieve greater efficiency, reduce waste, and ultimately improve their bottom line.
Types of Manufacturing Equipment: Classification Across Industries
Manufacturing equipment encompasses a wide array of machines and tools used across different industries to facilitate the production process. The types of manufacturing equipment can be classified into several categories based on their functionality and the industry they serve. For instance, in the automotive sector, you’ll find assembly lines equipped with robotic arms and conveyor systems designed for efficiency and precision. Conversely, the food industry relies heavily on processing machines such as mixers, ovens, and packaging equipment to meet health and safety standards while maximizing output.
Tips: When considering manufacturing equipment for your business, it's essential to evaluate your specific production needs. Analyze the volume of your output and the complexity of your processes to choose the right type of equipment. Additionally, investing in versatile machinery can provide the flexibility needed to adapt to changing demands.
In the textile sector, manufacturing equipment includes looms, sewing machines, and dyeing apparatus that ensure high-quality fabric production. Similarly, the electronics industry utilizes automated assembly machines and testing devices to streamline production while maintaining quality control. By understanding the various types of manufacturing equipment and their applications, businesses can optimize their production workflows and enhance overall efficiency.
What is Manufacturing Equipment? Types, Uses, and Benefits Explained
| Type of Equipment | Uses | Benefits | Industries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Robots | Automating assembly and packaging processes | Increased efficiency and precision | Automotive, Electronics |
| CNC Machines | Cutting, milling and drilling materials | High accuracy and repeatability | Aerospace, Metal Fabrication |
| 3D Printers | Creating prototypes and finished products | Reduced material waste and flexibility | Consumer Goods, Healthcare |
| Injection Molding Machines | Producing plastic parts | High volume production efficiency | Consumer Products, Automotive |
| Conveyor Systems | Transporting materials and products | Improved workflow and safety | Food, Packaging |
| Welding Machines | Joining metal parts | Strong joints and high durability | Construction, Manufacturing |
Common Uses of Manufacturing Equipment in Production Processes
Manufacturing equipment plays a crucial role in various production processes across multiple industries. Its applications span from the automotive sector to electronics and food processing. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global market for manufacturing equipment is expected to grow from $1,020 billion in 2020 to $1,500 billion by 2027, demonstrating the increasing reliance on advanced manufacturing technologies.
One of the common uses of manufacturing equipment is in assembly line production, where machines such as conveyors and robotic arms facilitate the efficient assembly of products. These systems significantly increase productivity and reduce labor costs. Research indicates that automated assembly lines can improve throughput by up to 50%, allowing manufacturers to meet rising consumer demand without compromising quality. Additionally, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are widely utilized in sectors like aerospace and automotive, enabling precision machining that enhances product quality and reduces waste.
Another essential application of manufacturing equipment is in quality control processes. Tools such as laser scanners and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) are integrated into production processes to ensure product specifications are met consistently. The implementation of such equipment has been shown to lower defect rates by over 30%, ultimately leading to increased customer satisfaction and reduced costs associated with returns and rework. As industries continue to evolve, the strategic use of manufacturing equipment will remain vital to achieving operational excellence.
Manufacturing Equipment Usage in Various Industries
Benefits of Utilizing Advanced Manufacturing Equipment Technologies
The integration of advanced manufacturing equipment technologies has revolutionized the production landscape, offering numerous benefits that enhance efficiency and productivity. One of the primary advantages is the significant improvement in precision and quality. Modern machinery, equipped with advanced sensors and automation capabilities, allows for tighter tolerances and consistency in manufacturing processes. This results in fewer defects and a reduction in waste, which not only increases the reliability of products but also enhances customer satisfaction.
Moreover, advanced manufacturing equipment often leads to streamlined operations. Automation reduces the need for manual intervention, which minimizes human error and allows workers to focus on more complex tasks that add greater value. This shift not only optimizes labor resources but also facilitates faster production cycles, enabling companies to respond more swiftly to market demands. Additionally, the implementation of smart technologies can provide real-time data analysis, further empowering manufacturers to make informed decisions and improve overall operational efficiency. As a result, organizations that embrace these technologies can gain a competitive edge in an increasingly demanding global market.
Industry Trends: Innovations Shaping the Future of Manufacturing Equipment
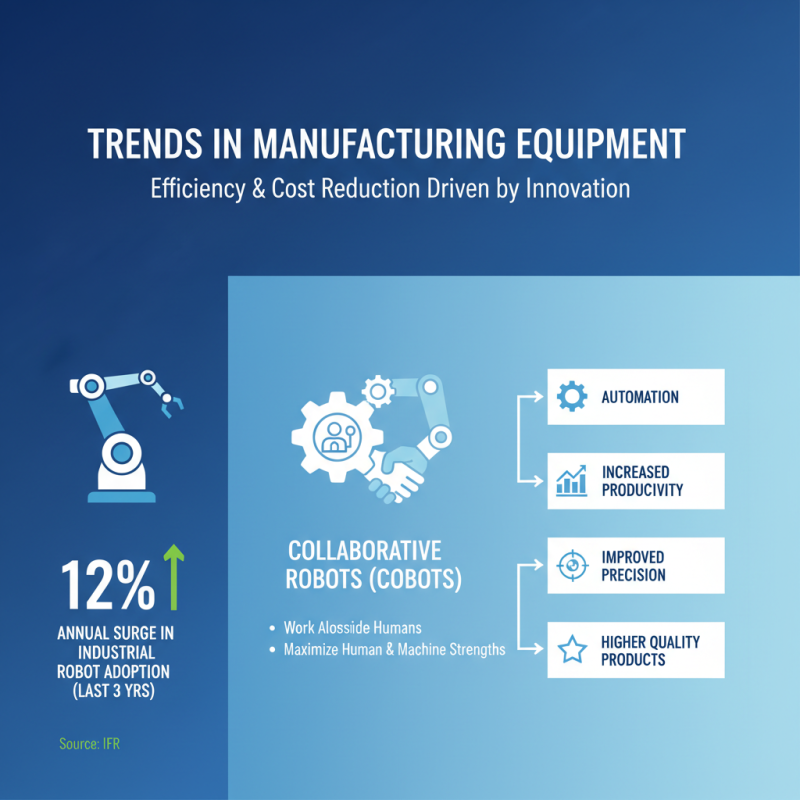
Recent trends in manufacturing equipment are being shaped by cutting-edge innovations that focus on increasing efficiency and reducing costs. According to a report by the International Federation of Robotics, the adoption of industrial robots has surged by 12% annually over the last three years, reflecting a significant shift towards automation in manufacturing. This transition not only enhances productivity but also improves precision, resulting in higher quality products. Industries are increasingly investing in collaborative robots (cobots), which are designed to work alongside human operators, thereby maximizing both human and machine strengths in manufacturing processes.
In addition to automation, advancements in smart technology and the Internet of Things (IoT) are revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape. A study by PwC anticipates that smart manufacturing could contribute up to $3.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030. By integrating IoT devices, manufacturers can monitor equipment performance in real-time, predict maintenance needs, and streamline operations. Data analytics allows for better decision-making, enabling manufacturers to adapt quickly to changing market demands. The utilization of artificial intelligence in manufacturing processes further optimizes production lines, creating a more responsive and flexible manufacturing environment. As these innovations continue to develop, the future of manufacturing equipment looks poised for remarkable transformation, promising increased competitiveness and sustainability in the industry.
Related Posts
-

2025 Top 5 Industrial Equipment Trends Transforming the Manufacturing Sector
-

2025 How to Choose the Best Industrial Equipment for Optimal Efficiency
-

What is Laser Cutting and How Does It Work for Various Materials
-

Unlocking Efficiency How Nesting Software Revolutionizes Material Cutting Processes
-

Exploring the Future of Metal Cutting Technologies: Trends, Innovations, and Market Insights for 2024
-

How to Choose the Right Laser Cutting Service for Your Project Needs