What is Sheet Metal Cutting? Techniques, Benefits, and Applications Explained
Sheet metal cutting is a vital process in various industries, serving as a foundational step in the fabrication and manufacturing of parts and products. According to the latest report from the Sheet Metal and Fabrication Industry Association, the global sheet metal cutting market is projected to grow by 5.4% annually over the next five years, driven by increased demand in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. This growth highlights the importance of understanding the various techniques, benefits, and applications associated with sheet metal cutting.
Expert in the field, Dr. Amelia Harper, emphasizes the significance of innovative cutting techniques for maintaining competitive advantage. She states, “Efficient sheet metal cutting not only enhances production speed but also improves precision, which is essential for high-quality manufacturing.” With advancements in technology, including laser and waterjet cutting, the processes have become more efficient and versatile, allowing manufacturers to meet specific design requirements while reducing material waste. This introduction aims to explore the methodologies used in sheet metal cutting, as well as its numerous applications across different industries, showcasing its critical role in modern manufacturing.

What is Sheet Metal Cutting? An Overview of Techniques and Processes

Sheet metal cutting is a crucial process in various manufacturing sectors, encompassing numerous techniques and methods tailored to specific applications. Among the primary cutting methods are shearing, laser cutting, water jet cutting, and plasma cutting. Shearing involves the use of straight blades that apply force to create a clean cut through the metal sheet, ideal for producing simple shapes with straight edges. Laser cutting, on the other hand, employs focused light beams to vaporize material precisely, allowing for intricate detailing and complex shapes that traditional methods may struggle to achieve.
Each technique offers distinct advantages and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the project. Water jet cutting, for instance, is known for its ability to cut through thick materials without introducing heat, preserving the integrity of sensitive components. Plasma cutting is favored for its speed and efficiency in dealing with thicker metals, making it an excellent choice for industrial applications. Understanding these techniques not only aids in selecting the appropriate method but also enhances the quality and precision of the finished product, showcasing the versatility of sheet metal cutting in contemporary manufacturing.
Key Techniques in Sheet Metal Cutting: Shearing, Laser, and Plasma
Sheet metal cutting is a critical process in various manufacturing sectors, allowing for the precise shaping and sizing of metal parts. Among the diverse techniques employed, shearing, laser, and plasma cutting stand out for their unique capabilities and applications. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global sheet metal cutting market was valued at approximately $7.6 billion in 2020 and is expected to reach $9.0 billion by 2025, reflecting an increasing demand for efficient and precise cutting technologies.
Shearing is a traditional cutting method that involves applying a significant force to metal sheets, resulting in a clean cut without the loss of material. This technique is widely adopted due to its speed and precision, making it suitable for large-scale operations. In comparison, laser cutting utilizes focused beams of light to melt or vaporize metal, achieving highly intricate designs with minimal thermal distortion. Data from Research and Markets reveals that the laser cutting market alone is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.0% from 2021 to 2026, emphasizing its role in modern manufacturing environments.
Plasma cutting, on the other hand, leverages ionized gas to cut through metals at high speeds, making it ideal for thicker materials and complex profiles. Industry analysis indicates that the plasma cutting segment is gaining traction in sectors such as aerospace and automotive, where precision and adaptability are paramount. Furthermore, the versatility of these techniques allows manufacturers to optimize their production processes and minimize waste, enhancing overall efficiency in sheet metal fabrication.
What is Sheet Metal Cutting? Techniques, Benefits, and Applications Explained
| Technique | Description | Benefits | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shearing | A mechanical process that cuts flat sheets of metal using a knife. | Fast cutting speed, minimal material waste, and cost-effective. | Automotive parts, frames, and general fabrication. |
| Laser Cutting | Utilizes a focused laser beam to cut materials with high precision. | High accuracy, complex shapes possible, and clean edges. | Aerospace, electronics, and custom signage. |
| Plasma Cutting | Employs a high-velocity jet of ionized gas to cut through metal. | Versatile for thick materials and fast operation for heavy-duty cutting. | Shipbuilding, metal artwork, and industrial manufacturing. |
Benefits of Sheet Metal Cutting: Efficiency, Precision, and Cost-Effectiveness
Sheet metal cutting is a fundamental process in many manufacturing sectors, and its benefits are multifaceted. Efficiency is one of the primary advantages of sheet metal cutting techniques. According to the 2021 Market Research Report on Sheet Metal Fabrication, companies that implement advanced cutting methods can achieve up to a 30% reduction in processing time compared to traditional techniques. This acceleration in production allows manufacturers to respond more swiftly to market demands and minimizes downtime in workflows, thereby enhancing overall productivity.
In addition to efficiency, precision plays a crucial role in sheet metal cutting. Modern cutting technologies, such as laser and waterjet cutting, boast accuracy levels within 0.1 mm, which significantly reduces material waste. As noted in industry analyses, precision cutting processes allow for better design intricacy and less rework, leading to improved product quality. Furthermore, this accuracy in cutting not only ensures that components fit precisely as intended but also leads to greater cost-effectiveness—reducing both scrap rates and the need for costly adjustments during assembly. In fact, it has been reported that manufacturers can save up to 20% in overall costs through enhanced material utilization and lower operational expenses linked to waste reduction.
Benefits of Sheet Metal Cutting
Industry Applications of Sheet Metal Cutting: Automotive, Aerospace, and Construction
Sheet metal cutting is a fundamental process utilized across various industries, most notably in automotive, aerospace, and construction sectors. In the automotive industry, precision cutting techniques are essential for creating components such as body panels and structural elements. These components must meet stringent safety and performance standards, requiring advanced cutting methods that provide both accuracy and efficiency. Innovations in laser and waterjet cutting technologies enable manufacturers to produce complex shapes and designs while minimizing material wastage, ultimately leading to more sustainable practices.
Similarly, the aerospace industry relies heavily on sheet metal cutting processes to fabricate lightweight yet durable parts that are critical for aircraft performance. Techniques such as CNC machining and plasma cutting are commonly employed to achieve the intricate designs necessary for various aircraft components. The ability to cut with high precision and to maintain tight tolerances is vital in reducing aircraft weight and improving fuel efficiency, making sheet metal cutting a cornerstone of modern aerospace engineering.
In the construction sector, sheet metal cutting is pivotal in producing architectural elements, HVAC ducts, and roofing materials. The use of efficient cutting techniques allows for the rapid creation of components that meet specific design requirements while adhering to building codes and safety regulations. By integrating automation and advanced software in the cutting process, construction firms can streamline operations, resulting in time and cost savings, which is crucial in today's fast-paced construction environment.
Future Trends in Sheet Metal Cutting: Automation and Advanced Technologies
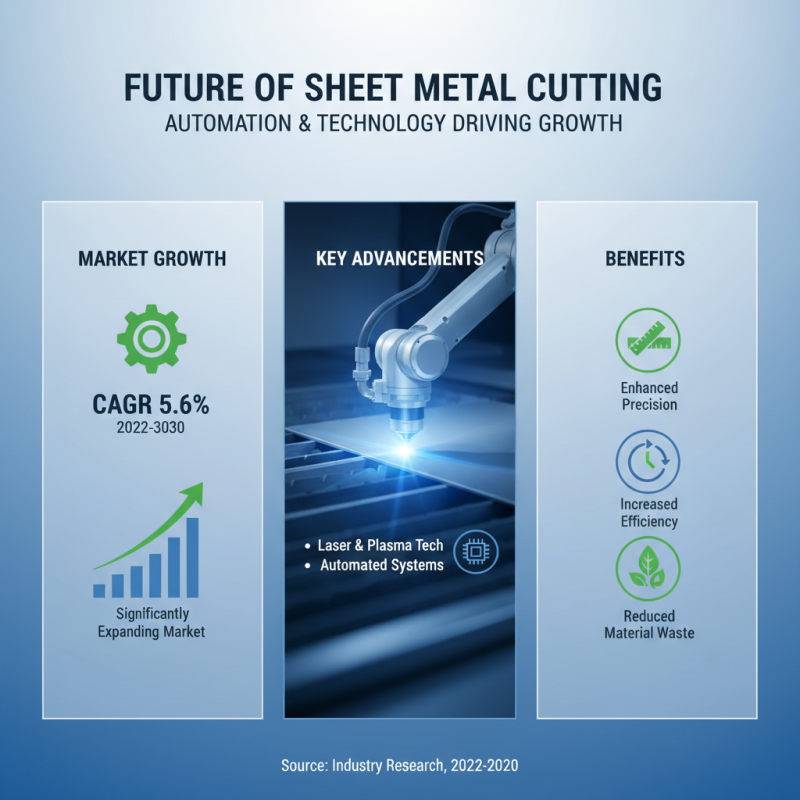
The landscape of sheet metal cutting is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in automation and technology. As industries increasingly adopt cutting-edge solutions, research indicates that the sheet metal fabrication market is projected to grow significantly, with an expected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5.6% from 2022 to 2030. Automation plays a pivotal role in this transformation, enabling manufacturers to enhance precision and efficiency while reducing labor costs. Automated cutting systems equipped with laser and plasma technologies ensure high throughput and accuracy, minimizing material waste—a crucial factor in today’s environmentally-conscious manufacturing practices.
Furthermore, the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning into sheet metal cutting processes is paving the way for smarter operations. These technologies facilitate predictive maintenance, optimize cutting paths, and improve overall operational efficiency. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global industrial automation market is expected to reach over $300 billion by 2026, underscoring the significant investment industries are making towards embracing automation in their manufacturing processes. As competition heightens, companies that harness these innovative technologies are likely to gain a substantial edge in productivity and cost management in the coming years.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Tips for Sheet Metal Bending Techniques You Need to Know
-

2025 Top 10 Water Jet Cutting Machines for Precision and Efficiency
-

How to Maximize Your Efficiency with Almacam Software for Optimal Results
-

What is a Sheet Metal Laser Cutting Machine? Benefits and Applications Explained
-

Maximize Fabrication Efficiency: The Rise of Sheet Metal Nesting Software in 2025
-

Top Benefits of Using a Laser Cutting Machine for Your Projects